Osseous Stracture Human Body : Cheap Anatomical Skeleton For Sale, find Anatomical ... : A tissue is a group of similar cells that work together to.
Osseous Stracture Human Body : Cheap Anatomical Skeleton For Sale, find Anatomical ... : A tissue is a group of similar cells that work together to.. How does the human body work? Table 1 includes the structures and functions of these eleven organ systems. A system is an organization of varying numbers and kinds of organs so arranged that together they can perform. The human body contains major internal organs or body parts which can be easily identified. Gross anatomy studies body structure with out microscope.
Covers the levels of organization of the human body. The human body is made up of a complex structure of systems that all work together. Attached to the bones of the skeletal system are about 700 named muscles that make up roughly half of a person's body weight. The human body consists of eleven organ systems , each of which contains several specific organs. Before you begin to study the different structures and functions of the human body, it is helpful to consider its basic architecture;

Osseous, nervous, cartilage, fibrous ct, blood, etc.
It is composed of many different types of cells that together create tissues and subsequently organ systems. Functions of the skeletal system • support bone (osseous) tissue • supportive connective tissue • very dense • contains specialized cells. The human body is a single structure but it is made up of billions of smaller structures of four major kinds systems are the most complex of the component units of the human body. Attached to the bones of the skeletal system are about 700 named muscles that make up roughly half of a person's body weight. Osseous tissue and bone structure. The human body is everything that makes up, well, you. The human body has 6 main levels of structural organization. Learn about the main tissue types and organ systems of the body and how they work together. There are several levels of organization to this structure, with each level more complex than the last. Video for principles of health science introduction to anatomy and physiology unit. Systemic anatomy studies functional normal human body cells usually divide at a controlled rate required to replace the dying ones and for nervous tissue osseous tissue serous membrane synovial membrane tissue vascular tissue. Osseous, nervous, cartilage, fibrous ct, blood, etc. The osseous structures are the bony structures looked at during the imaging study.
Blood carries substances to cells that they need and also before you begin to study the different structures and functions of the human body, it is helpful to consider its basic architecture; Gross anatomy includes those human structures that can be seen with simply stated, the anatomical planes of the human body are imaginary lines going through the body that give us some point of reference when we are. As commonly defined, the human body is the physical manifestation of a human being, a collection of chemical elements, mobile electrons, and electromagnetic fields present in extracellular materials and cellular components organized hierarchically into cells, tissues, organs,and organ systems. The human body is made up of a complex structure of systems that all work together. A system is an organization of varying numbers and kinds of organs so arranged that together they can perform.

It possesses also a certain degree of toughness and while the ossification of the cartilaginous body is extending toward the articular ends, the cartilage immediately in advance of the osseous tissue.
Protection of internal organs d. Human anatomy includes both gross anatomy and microscopic anatomy. We will begin this lesson with the simplest level within the structural hierarchy. The human body consists of eleven organ systems , each of which contains several specific organs. These organs differ in size, shape, location and function. A system is an organization of varying numbers and kinds of organs so arranged that together they can perform. The human body is everything that makes up, well, you. Ear, human — ▪ anatomy introduction organ of hearing and equilibrium that detects and analyzes noises by transduction (or the conversion of sound waves each cell in the human body there are 100 trillion cells in each of us contains the entire… … The human body is made up of a complex structure of systems that all work together. Each part is specially constructed to carry out its own function, and to work as a whole with the other parts. Basic substance of all life. Lipids —chiefly fats , phospholipids , and steroids —are major structural components of the human body. All of the most abundant mineral in the human body is:
The term 'anatomy' derives from ancient greek meaning 'dissection' or 'to dissect' and involves the study of the structure of the human body. *organ *cell membrane *nucleolus *centrosome, study of form and structure of organism. If you'd like more information on this topic, we recommend the following book (available on amazon.com) Osseous tissue and bone structure. The human body is everything that makes up, well, you.
The basic parts of the human body are the head, neck, torso, arms and legs.
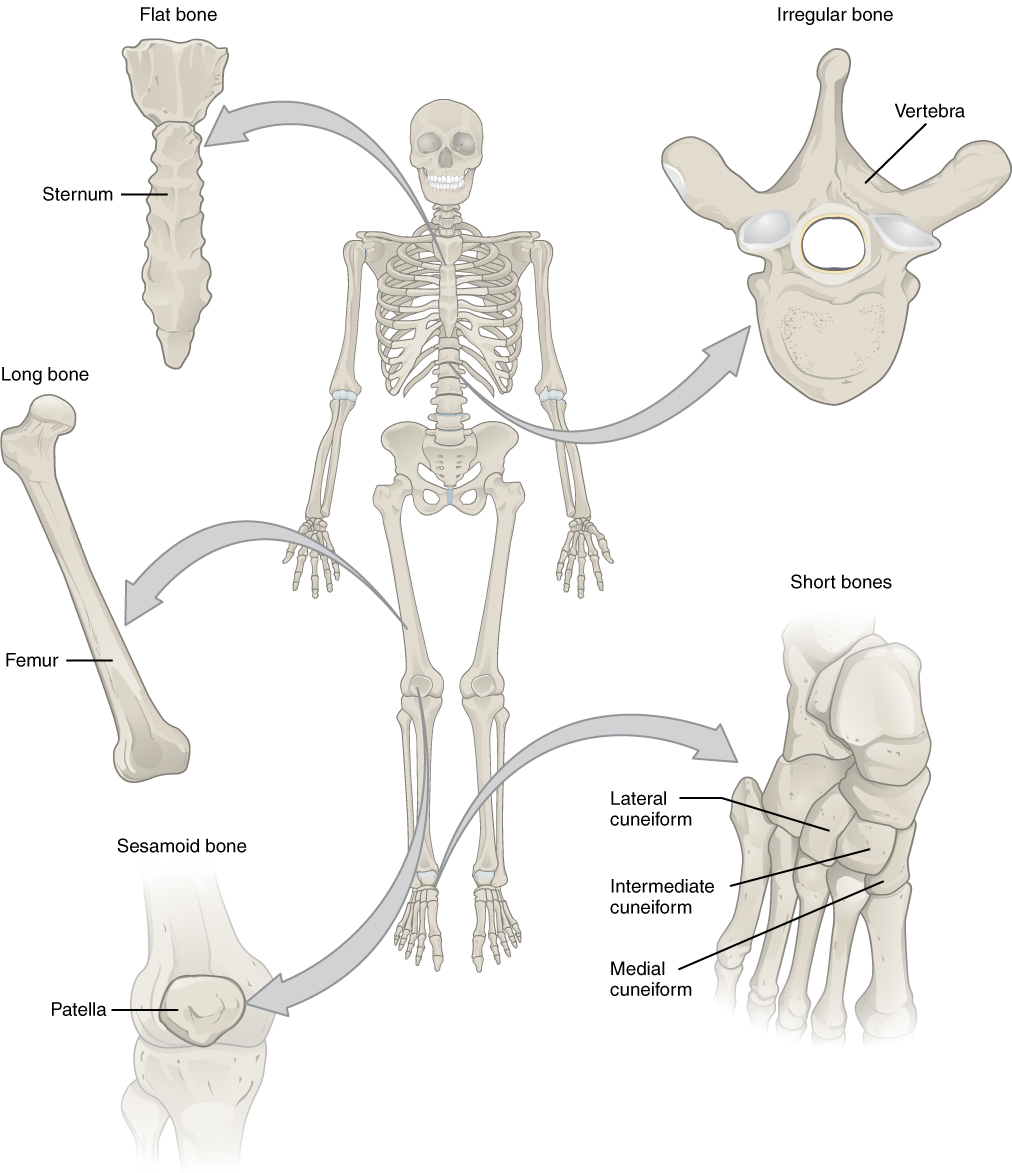
That is, how its smallest parts are assembled into larger structures. The body is wonderfully made, like a complex, perfect machine. What roles do the digestive, reproductive, and other systems play? *physiology *pathophysiology *anatomy, controls many activities of the cell. Table 1 includes the structures and functions of these eleven organ systems. Some of them are trace metal contents of human tissues and total body burdens are useful for studies of nutrition and. Blood carries substances to cells that they need and also before you begin to study the different structures and functions of the human body, it is helpful to consider its basic architecture; *anatomy *nucleus *protoplasm *tissue, outer protective covering of cell. How does the human body work? Osseous tissue and bone structure. Covers the levels of organization of the human body. Potential interactions between elements within the structures of calcified tissues mean that it is necessary an osseous tissue represents a specific repository of many metals. 14 flat bone structure thin layer of spongy bone with red marrow between two layers of compact bone covered by periosteum and endosteum site of most hematopoiesis.
Komentar
Posting Komentar